Disposable examination gown (40gsm)
R23.99
Disposable hospital wear refers to medical clothing and accessories that are designed for single-use purposes and are intended to be discarded after each use. These items are crucial in maintaining a sterile and hygienic environment in healthcare settings, helping to prevent the spread of infections and diseases.
Examples of Disposable hospital wear include:
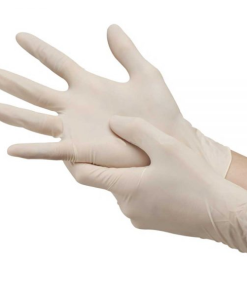
Disposable Gloves: Made of latex, nitrile, or vinyl, these gloves are worn by healthcare professionals to protect themselves and patients from cross-contamination during examinations and medical procedures.
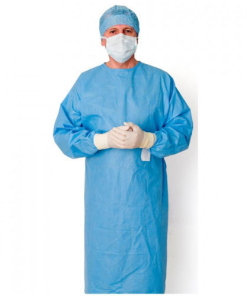
Surgical Gowns: These gowns are worn by surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare personnel during Surgical procedures to provide a protective barrier against potential contaminants.